
Introdução à seleção Classificar em Java
A opção Classificação em Java é um método de classificação que encontra continuamente o menor elemento na parte não classificada e o mantém no início (para classificação em ordem crescente). O processo será repetido até que a matriz de entrada seja classificada. Além disso, em Selection Sort, dividiremos a matriz de entrada em duas sub-matrizes, em que uma matriz é usada para elementos classificados e outra matriz é para elementos não classificados. No começo, não haverá elementos na sub-matriz classificada. Vamos ver o trabalho da seleção em detalhes na seção a seguir.
Como a classificação de seleção funciona em Java
A classificação por seleção funciona de maneira simples, onde mantém duas sub-matrizes da matriz de entrada. Eles são:
- Subarray classificada para manter os elementos classificados
- Subarray não classificado para manter os elementos não classificados.
Algoritmo:
A seguir está o algoritmo usado para a classificação Selection
- Defina o ponteiro mínimo (MIN) para o local 0.
- Encontre o menor elemento da lista de elementos na matriz
- Troque o elemento mínimo pelo local 0
- Mova o ponteiro MIN para a próxima posição
- Repita o processo até que a matriz de entrada seja classificada.
Vamos entender a classificação por seleção com um exemplo. A seguir, é apresentada a matriz de entrada que deve ser classificada. Os elementos na cor Negrito Azul farão parte da matriz classificada.

Etapa 1 : defina o ponteiro MIN para o primeiro local. Portanto, o ponteiro MIN aponta para 15.
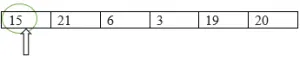
Menor: = 15
Etapa 2 : encontre o menor elemento comparando-o com o restante dos elementos. Comparando 15 e 21, 15 é o menor. Portanto, o menor não mudará neste caso.
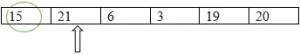
Menor: = 15
Comparando 15 e 6, 6 é o menor.
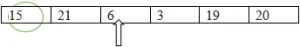
Menor: = 6
Comparando 6 e 3, 3 é o menor.
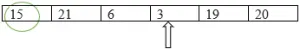
Menor: = 3
3 será menor também neste caso, pois 19 é maior que 3.
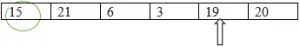
Menor: = 3
Menor: = 3
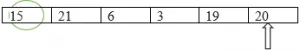
Finalmente, nesta iteração, 3 é considerado o menor.
Etapa 3 : troque o menor elemento pelo elemento no local 0.

Etapa 4: Incremente o ponteiro MIN para a próxima posição.

Etapa 5: encontre o próximo menor elemento comparando-o com o restante dos elementos.

Menor: = 21
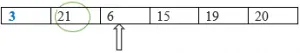
Menor: = 6
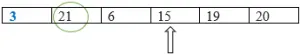
Menor: = 6

Menor: = 6
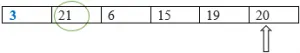
Menor: = 6
Etapa 6: troque o menor elemento pelo elemento no local 1.

Repita o processo até que uma matriz classificada seja formada, como mostrado abaixo.

Exemplos para implementar a classificação de seleção em Java
Como já mencionado acima, a classificação de seleção é baseada em encontrar o mínimo e a troca. Agora, vamos ver como implementar a classificação de seleção usando Java.
Programa Java para classificar os elementos em uma matriz usando a classificação de seleção
import java.util.*;
public class SelSortExample (
//Method that implements Selectionsort
public static void selsort(int() arr)
(
int n=arr.length; //length of the array
for(int i=0;i (
int MIN=i; //set the first position as minimum
System.out.println("Sorting based on Number "+(i+1));
//Find the smallest element by comparing with the element in MIN position
for(int j=i+1;j (
System.out.println("Comparing "+ arr(MIN) + " and " + arr(j));
if(arr(j) (
System.out.println(arr(MIN) + " is greater than " + arr(j) );
MIN=j;
)
)
//Swap the smallest element with element in MIN position
int temp=arr(i);
arr(i)=arr(MIN);
arr(MIN)=temp;
)
)
public static void main(String() args) (
int() arr= (15, 21, 6, 3, 19, 20); // input array
System.out.println("Elements in the array before Sorting: "+ Arrays. toString (arr));
selsort (arr);//calling the selection sort method
System.out.println("Elements in the array after Sorting: "+Arrays. toString (arr));
)
)import java.util.*;
public class SelSortExample (
//Method that implements Selectionsort
public static void selsort(int() arr)
(
int n=arr.length; //length of the array
for(int i=0;i (
int MIN=i; //set the first position as minimum
System.out.println("Sorting based on Number "+(i+1));
//Find the smallest element by comparing with the element in MIN position
for(int j=i+1;j (
System.out.println("Comparing "+ arr(MIN) + " and " + arr(j));
if(arr(j) (
System.out.println(arr(MIN) + " is greater than " + arr(j) );
MIN=j;
)
)
//Swap the smallest element with element in MIN position
int temp=arr(i);
arr(i)=arr(MIN);
arr(MIN)=temp;
)
)
public static void main(String() args) (
int() arr= (15, 21, 6, 3, 19, 20); // input array
System.out.println("Elements in the array before Sorting: "+ Arrays. toString (arr));
selsort (arr);//calling the selection sort method
System.out.println("Elements in the array after Sorting: "+Arrays. toString (arr));
)
)import java.util.*;
public class SelSortExample (
//Method that implements Selectionsort
public static void selsort(int() arr)
(
int n=arr.length; //length of the array
for(int i=0;i (
int MIN=i; //set the first position as minimum
System.out.println("Sorting based on Number "+(i+1));
//Find the smallest element by comparing with the element in MIN position
for(int j=i+1;j (
System.out.println("Comparing "+ arr(MIN) + " and " + arr(j));
if(arr(j) (
System.out.println(arr(MIN) + " is greater than " + arr(j) );
MIN=j;
)
)
//Swap the smallest element with element in MIN position
int temp=arr(i);
arr(i)=arr(MIN);
arr(MIN)=temp;
)
)
public static void main(String() args) (
int() arr= (15, 21, 6, 3, 19, 20); // input array
System.out.println("Elements in the array before Sorting: "+ Arrays. toString (arr));
selsort (arr);//calling the selection sort method
System.out.println("Elements in the array after Sorting: "+Arrays. toString (arr));
)
)import java.util.*;
public class SelSortExample (
//Method that implements Selectionsort
public static void selsort(int() arr)
(
int n=arr.length; //length of the array
for(int i=0;i (
int MIN=i; //set the first position as minimum
System.out.println("Sorting based on Number "+(i+1));
//Find the smallest element by comparing with the element in MIN position
for(int j=i+1;j (
System.out.println("Comparing "+ arr(MIN) + " and " + arr(j));
if(arr(j) (
System.out.println(arr(MIN) + " is greater than " + arr(j) );
MIN=j;
)
)
//Swap the smallest element with element in MIN position
int temp=arr(i);
arr(i)=arr(MIN);
arr(MIN)=temp;
)
)
public static void main(String() args) (
int() arr= (15, 21, 6, 3, 19, 20); // input array
System.out.println("Elements in the array before Sorting: "+ Arrays. toString (arr));
selsort (arr);//calling the selection sort method
System.out.println("Elements in the array after Sorting: "+Arrays. toString (arr));
)
)
Saída de amostra:

No programa acima, temos dois métodos - métodos principais e método de classificação de venda. O método principal chama o método de classificação de venda que passa a matriz de entrada como argumento. O elemento mínimo será identificado e trocado pelo elemento apontado por MIN.
A classificação de seleção também pode ser usada onde a matriz de entrada não está definida no código. Vamos ver como ele funciona usando o programa abaixo.
Programa Java para classificar os elementos usando a classificação de seleção
import java.util.*;
public class SelectionSortExample
(
public static void main(String args())
(
int n, i, j, tempvar;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //To take the input from user
System.out.print("Enter the size of array : \n");
n = sc.nextInt();
int array() = new int(n); //initialising the array
System.out.print("Enter the elements that need to be inserted in the array : \n");
//inserting the elements to the array
for(i=0; i (
array(i) = sc.nextInt();
)
System.out.print("array before Sorting: \n"+ Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.print("\nSorting begins here..\n");
for(i=0; i (
for(j=i+1; j (
if(array(i) > array(j))
(
tempvar = array(i);
array(i) = array(j);
array(j) = tempvar;
)
)
)
System.out.print("Array after Sorting is :\n");
for(i=0; i (
System.out.print(array(i)+ " ");
)
)
)import java.util.*;
public class SelectionSortExample
(
public static void main(String args())
(
int n, i, j, tempvar;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //To take the input from user
System.out.print("Enter the size of array : \n");
n = sc.nextInt();
int array() = new int(n); //initialising the array
System.out.print("Enter the elements that need to be inserted in the array : \n");
//inserting the elements to the array
for(i=0; i (
array(i) = sc.nextInt();
)
System.out.print("array before Sorting: \n"+ Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.print("\nSorting begins here..\n");
for(i=0; i (
for(j=i+1; j (
if(array(i) > array(j))
(
tempvar = array(i);
array(i) = array(j);
array(j) = tempvar;
)
)
)
System.out.print("Array after Sorting is :\n");
for(i=0; i (
System.out.print(array(i)+ " ");
)
)
)import java.util.*;
public class SelectionSortExample
(
public static void main(String args())
(
int n, i, j, tempvar;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //To take the input from user
System.out.print("Enter the size of array : \n");
n = sc.nextInt();
int array() = new int(n); //initialising the array
System.out.print("Enter the elements that need to be inserted in the array : \n");
//inserting the elements to the array
for(i=0; i (
array(i) = sc.nextInt();
)
System.out.print("array before Sorting: \n"+ Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.print("\nSorting begins here..\n");
for(i=0; i (
for(j=i+1; j (
if(array(i) > array(j))
(
tempvar = array(i);
array(i) = array(j);
array(j) = tempvar;
)
)
)
System.out.print("Array after Sorting is :\n");
for(i=0; i (
System.out.print(array(i)+ " ");
)
)
)import java.util.*;
public class SelectionSortExample
(
public static void main(String args())
(
int n, i, j, tempvar;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //To take the input from user
System.out.print("Enter the size of array : \n");
n = sc.nextInt();
int array() = new int(n); //initialising the array
System.out.print("Enter the elements that need to be inserted in the array : \n");
//inserting the elements to the array
for(i=0; i (
array(i) = sc.nextInt();
)
System.out.print("array before Sorting: \n"+ Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.print("\nSorting begins here..\n");
for(i=0; i (
for(j=i+1; j (
if(array(i) > array(j))
(
tempvar = array(i);
array(i) = array(j);
array(j) = tempvar;
)
)
)
System.out.print("Array after Sorting is :\n");
for(i=0; i (
System.out.print(array(i)+ " ");
)
)
)import java.util.*;
public class SelectionSortExample
(
public static void main(String args())
(
int n, i, j, tempvar;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //To take the input from user
System.out.print("Enter the size of array : \n");
n = sc.nextInt();
int array() = new int(n); //initialising the array
System.out.print("Enter the elements that need to be inserted in the array : \n");
//inserting the elements to the array
for(i=0; i (
array(i) = sc.nextInt();
)
System.out.print("array before Sorting: \n"+ Arrays.toString(array));
System.out.print("\nSorting begins here..\n");
for(i=0; i (
for(j=i+1; j (
if(array(i) > array(j))
(
tempvar = array(i);
array(i) = array(j);
array(j) = tempvar;
)
)
)
System.out.print("Array after Sorting is :\n");
for(i=0; i (
System.out.print(array(i)+ " ");
)
)
)
Saída de amostra:

Aqui, os elementos de entrada fornecidos pelo usuário serão comparados com a variável temporária e trocados. O processo será repetido até que uma matriz classificada seja formada.
Desempenho da classificação de seleção
Essa técnica de classificação é usada por sua simplicidade e por outras vantagens de desempenho em relação a outras técnicas de classificação.
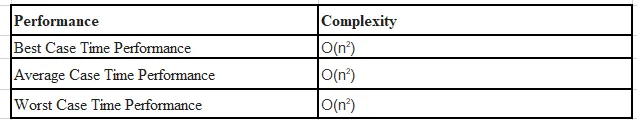
Conclusão
A classificação de seleção não funciona eficientemente em listas grandes, pois consome mais tempo para comparação. A classificação por seleção é um método no qual uma matriz de entrada será dividida em duas sub-matrizes para mantê-las classificadas e sem classificação. O elemento mínimo na matriz será trocado pelo elemento na primeira posição e o processo continuará até que uma matriz classificada seja formada.
Artigos recomendados
Este é um guia para a Sort Sort In Java. Aqui discutimos a introdução, trabalho e desempenho da seleção, juntamente com alguns exemplos. Você também pode consultar os seguintes artigos para saber mais -
- Mesclar classificação em Java
- Heap Sort In Java
- Copiar Construtor em Java
- Padrões de estrelas em Java
- Heap Sort em Python